服务级别的依赖
https://github.com/typeonce-dev/effect-getting-started-course
缺少一件事:为什么 PokeApiLive 没有对 PokemonCollection 和 BuildPokeApiUrl 的依赖?
const make = {
getPokemon: Effect.gen(function* () {
const pokemonCollection = yield* PokemonCollection;
const buildPokeApiUrl = yield* BuildPokeApiUrl;
const requestUrl = buildPokeApiUrl({ name: pokemonCollection[0] });
const response = yield* Effect.tryPromise({
try: () => fetch(requestUrl),
catch: () => new FetchError(),
});
if (!response.ok) {
return yield* new FetchError();
}
const json = yield* Effect.tryPromise({
try: () => response.json(),
catch: () => new JsonError(),
});
return yield* Schema.decodeUnknown(Pokemon)(json);
}),
};
export class PokeApi extends Context.Tag("PokeApi")<PokeApi, typeof make>() {
static readonly Live = Layer.succeed(this, make);
}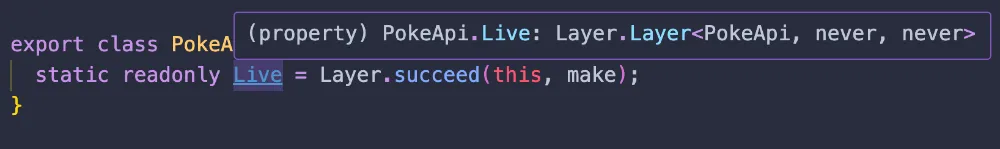
尽管使用了PokemonCollection和BuildPokeApiUrl,PokeApi.Live对它们没有依赖关系(Layer的第三个类型参数是never)
这回到了我们之前讨论的内容:依赖关系不在 PokeApi 上,而是在 getPokemon 函数上。
实际上,这意味着只有当我们使用 getPokemon 时才需要这些依赖关系。这不是服务本身的要求。
NOTE在我们的例子中,
MainLayer提供了PokemonCollection和BuildPokeApiUrl,因此一切都按预期工作。
const MainLayer = Layer.mergeAll(
PokeApi.Live,
PokemonCollection.Live,
BuildPokeApiUrl.Live,
PokeApiUrl.Live
);函数级别的依赖关系在只有1个函数需要它们时很有用。在实践中,通常将依赖关系提升到服务上,因为多个函数会使用相同的依赖关系:
将
PokemonCollection和BuildPokeApiUrl从getPokemon外部提取将服务
Context的定义更改为Effect.Effect.Success<PokeApi>由于
make现在是一个Effect,我们需要使用Layer.effect而不是Layer.succeed
PokeApi.ts
const make = Effect.gen(function* () {
/// 1️⃣ 将 `PokemonCollection` 和 `BuildPokeApiUrl` 从 `getPokemon` 外部提取
const pokemonCollection = yield* PokemonCollection;
const buildPokeApiUrl = yield* BuildPokeApiUrl;
return {
getPokemon: Effect.gen(function* () {
const requestUrl = buildPokeApiUrl({ name: pokemonCollection[0] });
const response = yield* Effect.tryPromise({
try: () => fetch(requestUrl),
catch: () => new FetchError(),
});
if (!response.ok) {
return yield* new FetchError();
}
const json = yield* Effect.tryPromise({
try: () => response.json(),
catch: () => new JsonError(),
});
return yield* Schema.decodeUnknown(Pokemon)(json);
}),
};
});
export class PokeApi extends Context.Tag("PokeApi")<
PokeApi,
/// 2️⃣ 将服务定义更改为 `Effect.Effect.Success<typeof make>`
Effect.Effect.Success<typeof make>
>() {
/// 3️⃣ 使用 `Layer.effect` 而不是 `Layer.succeed`
static readonly Live = Layer.effect(this, make);
}TIPEffect.Effect.Success
Effect.Effect.Success允许从任何Effect(第一个类型参数)中提取成功类型。
这是必需的,因为我们希望服务包含成功的方法,而不是用于创建它的 Effect。
最后一步是向 PokeApiLive 提供所需的依赖关系:
PokeApi.ts
export class PokeApi extends Context.Tag("PokeApi")<
PokeApi,
Effect.Effect.Success<typeof make>
>() {
static readonly Live = Layer.effect(this, make).pipe(
// 👇 记住:在 `Live` 内直接提供依赖关系
Layer.provide(Layer.mergeAll(PokemonCollection.Live, BuildPokeApiUrl.Live))
);
}此外,PokemonCollection 和 BuildPokeApiUrl 由 PokeApi 提供,PokeApiUrl 由 BuildPokeApiUrl 提供:
export class PokeApi extends Context.Tag("PokeApi")<
PokeApi,
Effect.Effect.Success<typeof make>
>() {
static readonly Live = Layer.effect(this, make).pipe(
// 👇 `PokemonCollection` 和 `BuildPokeApiUrl` 由 `PokeApi` 提供
Layer.provide(Layer.mergeAll(PokemonCollection.Live, BuildPokeApiUrl.Live))
);
}export class BuildPokeApiUrl extends Context.Tag("BuildPokeApiUrl")<
BuildPokeApiUrl,
({ name }: { name: string }) => string
>() {
static readonly Live = Layer.effect(
this,
Effect.gen(function* () {
const pokeApiUrl = yield* PokeApiUrl;
return ({ name }) => `${pokeApiUrl}/${name}`;
})
).pipe(
// 👇 `PokeApiUrl` 由 `BuildPokeApiUrl` 提供
Layer.provide(PokeApiUrl.Live)
);
}这意味着我们不需要在 MainLayer 中提供它们:
const MainLayer = Layer.mergeAll(
PokeApi.Live,
PokemonCollection.Live,
BuildPokeApiUrl.Live,
PokeApiUrl.Live
);MainLayer 只需要 PokeApi,因为它直接在 program 内使用。这是最终结果:
index.ts
import { Effect, Layer } from "effect";
import { PokeApi } from "./PokeApi";
const MainLayer = Layer.mergeAll(PokeApi.Live);
export const program = Effect.gen(function* () {
const pokeApi = yield* PokeApi;
return yield* pokeApi.getPokemon;
});
const runnable = program.pipe(Effect.provide(MainLayer));
const main = runnable.pipe(
Effect.catchTags({
FetchError: () => Effect.succeed("Fetch error"),
JsonError: () => Effect.succeed("Json error"),
ParseError: () => Effect.succeed("Parse error"),
})
);
Effect.runPromise(main).then(console.log);IMPORTANT组织完成
完成!现在我们组织了所有服务、层和它们的依赖关系。
每个服务实现在创建
Layer时都直接提供了自己的依赖关系。这允许拥有一个扁平的
MainLayer和单个mergeAll。每个依赖关系都在单独的文件中定义和提供,这样我们可以在将所有内容组合在一起之前专注于一个服务。全部类型安全!